How are intrauterine adhesions formed?
In particular, damage to the uterus may sometimes occur due to previous intrauterine procedures, abortion procedures, procedures due to pregnancy losses, procedures performed due to the placenta remaining in the uterus, surgeries or infections. These can also cause adhesions These damages in the uterus become permanent if the uterus cannot heal on its own and adhesions occur in places.
What clinical consequences do intrauterine adhesions cause?
Intrauterine adhesions will cause the uterus not to be fed enough, not to thicken and not to form enough space in the uterus. Thus, both the appropriate environment for the formation of pregnancy will not be created and the placenta placement in the continuation of pregnancy, that is, the growth of the peer to the appropriate place, will not occur. Thus, both difficulty in conceiving and recurrent pregnancy losses will occur.
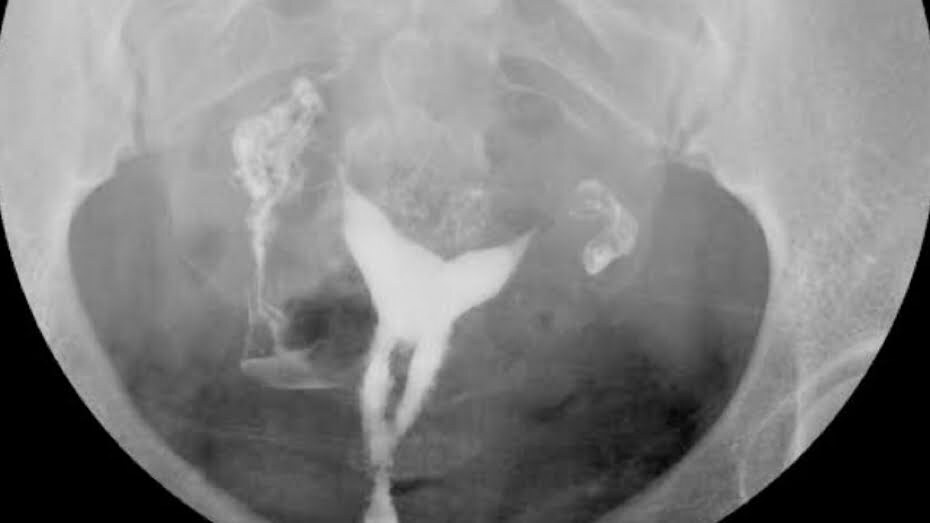
How are uterine adhesions detected?
In the absence of sufficient uterine thickness at certain times of the menstrual cycle, we can suspect it with ultrasound, but the clear diagnosis can be made by uterine film or hysteroscopy. In cases where uterine adhesion is suspected with uterine film, hysteroscopy, that is, entering the uterus with the help of an optical camera, will clarify the diagnosis.
How is the treatment of uterine adhesions performed?
The most important form of treatment here is hysteroscopy, that is, the places of the adhesions are determined by entering the uterus with the optical system and these adhesions are tried to be opened with the help of scissors or electric cautery. All this can be done under the guidance of ultrasound, so that the treatment will be more effective. After hysteroscopic opening of uterine adhesions, some special treatments, hormone treatments, some treatments that increase bleeding and gel applications into the uterus can be used.